【Business Process Management】
A Secret Sauce or Main Ingredient for
Technology Adoption Success?
2022/1/20
Author: Aqmar Zakaria
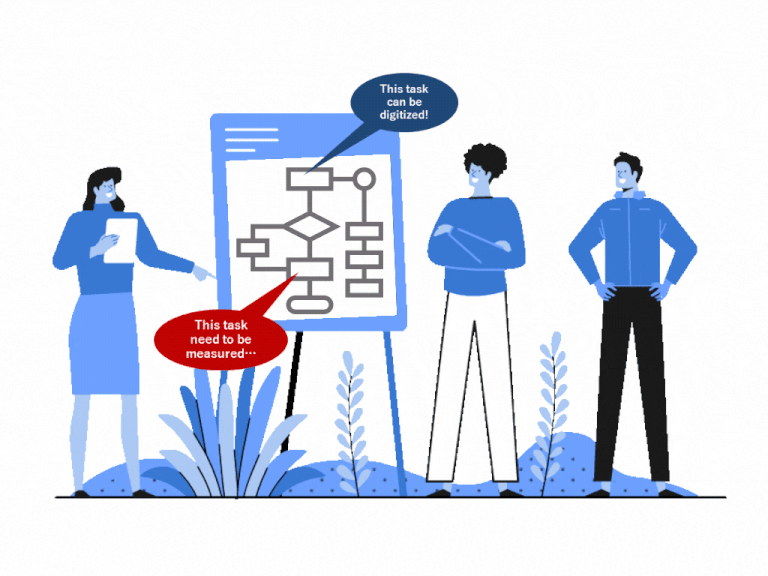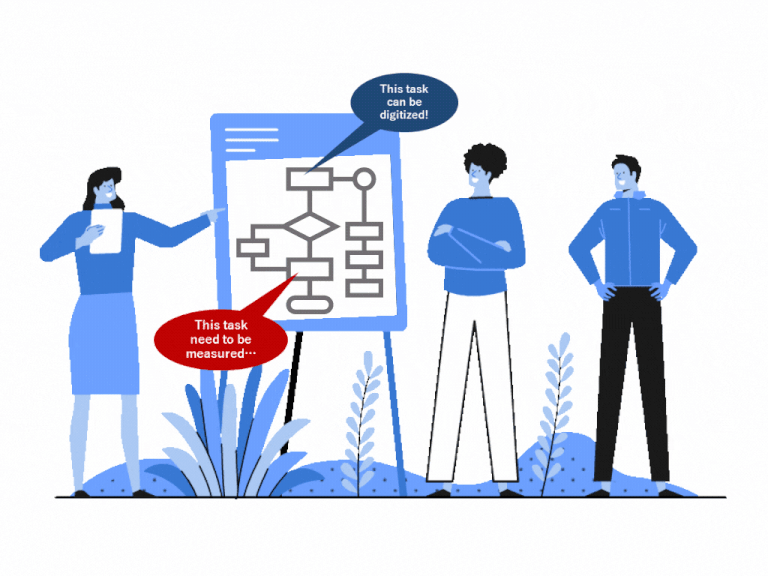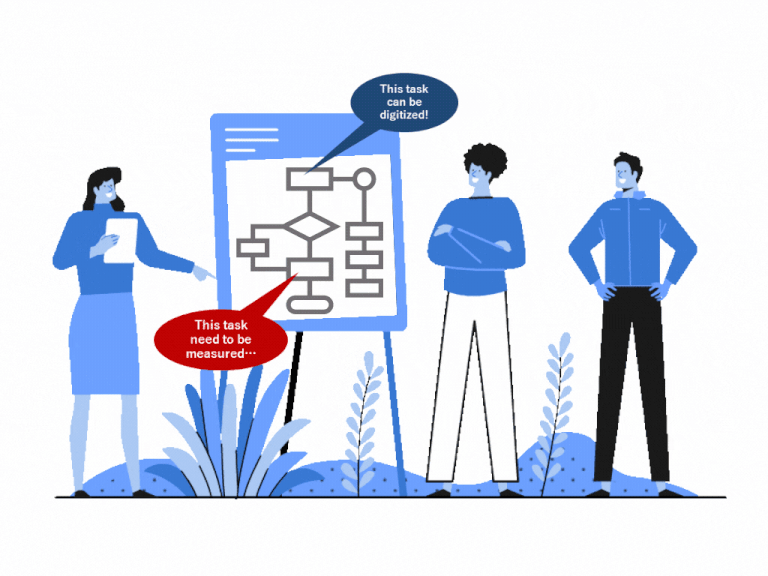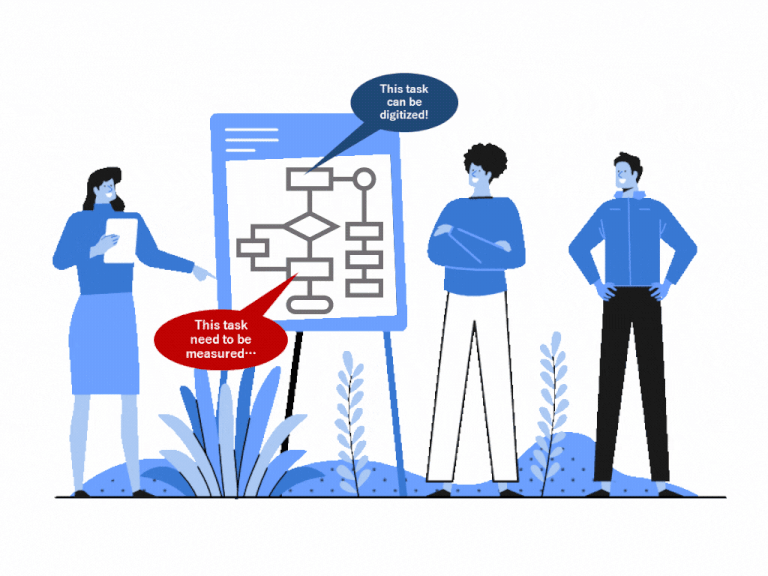
When I decided to shift from scientific research to consulting and joined Innovative Solutions Inc. (ISOL) 8 months ago, the question I had in mind is “Where I can have a career with a direct impact on the industry?” and “How I could make a difference?”. ISOL is a process-centric place in solving problems where I start learning to include process visibility in every project, I have been involved in.
During my first time experiencing using Business Process Management and Notation (BPMN) tool (Exhibit 1), called iGrafx, I realized that processes are the center of company operations and projects. Meaning that the company that can leverage BPMN tools and well comprehend their existing processes, at the same time have a good insight on what is happening in the business world, would be able to perceive opportunities to innovate, jumpstart, and drive growth.
In my current role as Associate DX Consultant, I learned that some legacy organizations in Japan have shifted from their legacy tools (for instance, paper-based documentation) and manual processes to data analytics technologies to thrive and stay resilient during this era of analytics and rapidly changing environment. These businesses believe data analytics is the key to accurate insight and the ability to make real-time decision-making.
Processes are one of the components in their transformation effort, where they begin with as-is process analysis and then design to-be process by incorporating digital technology. This type of gap analysis of as-is and to-be processes is an imperative part of the Business Process Management (BPM) strategy. Being able to map and visualize processes is important as I believe the process analysis would lead me to the potential part of operations to be transformed and eventually bring the analytics-driven culture to be realized in the company/organization. BPM is an essential skill acquired at ISOL that I will keep at my heart throughout my consulting career forward.
Below, I discuss BPM, various digital transformation efforts, the failure factors, and how BPM could secure the success of digital transformation efforts in organizations. Let’s start our investigation.
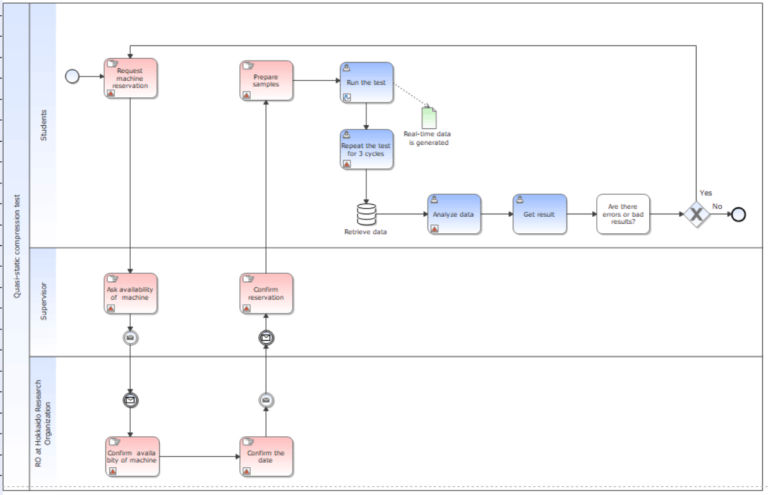
The fourth Industrial Revolution has been here for a while and has been forcing businesses to adapt to the related technology. Pandemic has accelerated the adoption of the technology by several years according to McKinsey [1]; 10+years for the Asia Pacific, 7 years for Europe, and 6 years for North America. IDC in their report, IDC FutureScape: Worldwide Digital Transformation 2021 Predictions [2] foresees the digital transformation investment to approach $6.8 trillion in the period from 2020 to 2023 as companies attempt to respond to the global pandemic and become more sustainable to endure unpredictable situations.
Despite high investment having been made on digital technology, most organizations failed to digitally “transform” and the investments have not paid off. This is due to the fact that the organizations are not capable to figure out decent processes to adopt the technology. As Professor Tomas Chamorro-Premuzic in his article [3] highlighted 5 essential components of an organization’s digital transformation are people, data, insights, action, and results. These components can be well incorporated if the organization has been prioritized process visibility in its operations. In my opinion, it is vital to leverage Business Process Management (BPM) method – which will be explained later – that has been existing in the business management discipline since the 2000s to align all components for an organization to successfully execute its digital transformation strategy.
What is BPM?
A business process is chains of activities and tasks performed by people or systems, once completed will contribute to business goals and support business strategy. BPM, according to Dumas et al. in their book Fundamentals of Business Process Management, is “the art and science of overseeing how work is performed in an organization to ensure consistent outcomes and to take advantage of improvement opportunities”. BPM is a discipline that covers how people discover, model, analyze, measure, and improve processes to create a more cost-efficient organization, reduce execution times, and minimize error rates.
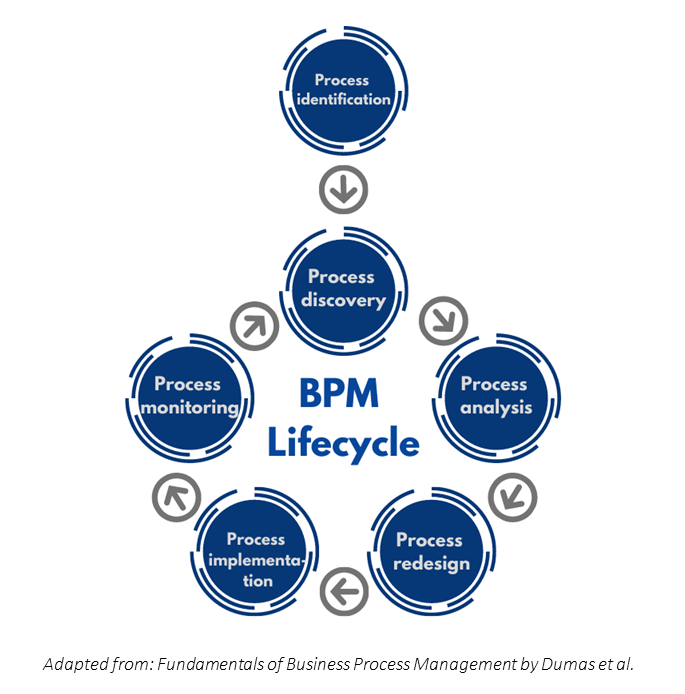
A BPM lifecycle is a continuous effort that consists of 6 stages namely, process identification, process discovery, process analysis, process redesign, process implementation, and process monitoring as shown in Exhibit 2.
In each stage, process visibility and clarity are important to accurately monitor the operations across the organizations while aligning the processes with business goals. The knowledge could help the organization to establish a competitive advantage when potential process problems can be identified or know which process can be democratized for a better strategy. In addition, BPM could help top management to comprehend business complexity, analyze process performance, continuously improve and innovate processes in one’s organization [4].
Ambidextrous BPM
There are two approaches to BPM; exploitative and explorative approaches. BPM has been used to exploit existing business processes and good at supporting problem-driven innovation. On the one hand, exploitative BPM has been utilized to eliminate waste, variation, bottlenecks, manual work, and non-conformance. On the other hand, explorative BPM is always driven by an outside-in and proactive approach.
In this digital era, process exploration would enable businesses and organizations to apply the latest digital technologies to existing processes and bring transformational innovation into organizations for business sustainability. Explorative BPM is beneficial for a business to stay relevant in today’s fast-paced digital world. However, it is undeniable that exploitative BPM is also important in business continuity. As Helbin & Looy noted in their literature review, “Business Process Management ambidexterity is a nascent concept providing a philosophy and framework for organizations to radically innovate their business processes, while maintaining their capabilities in process efficiency and operational excellence”.
Therefore, ambidextrous BPM is to strike the balance between exploitation and exploration targeting the business today’s efficiency and tomorrow’s revenue. The term ambidextrous BPM has been coined by Rosemann et al. to respond to digitization efforts in society and businesses to maximize the opportunity-driven as well as problem-driven capabilities of BPM and to manage innovations in the digital age (Exhibit 3).
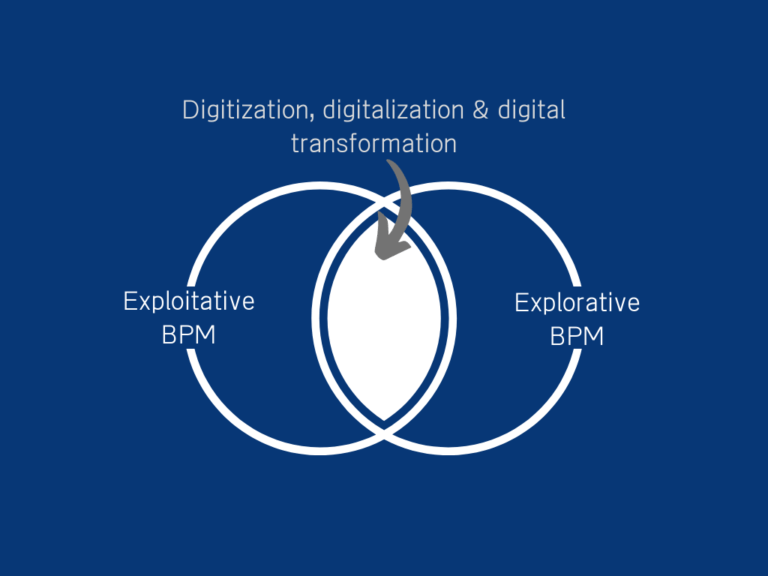
Digitization, digitalization, and digital transformation
Digital transformation has been reported in many articles and the terms digitization and digitalization join the fray. Digitization and digital transformation have been mentioned from the beginning of this article. So, what is exactly the difference between digitization, digitalization, and digital transformation? Digitization is simply a shift from analog to digital in handling information and digitalization according to Gartner is leveraging digitized information and digital technologies to improve business processes in delivering value. Meanwhile, digital transformation is beyond digitalization and refers to how an organization or a business transform to democratize technology, processes, and talents to proactively respond to disruptive change.
An example of a digital transformation effort that ISOL has been involved in is ASKUL Logistics (a logistic service provider) transformation of employees’ task management in their warehouses from a paper basis to a digital platform which we called Task Tracking System (TTS). With TTS, employees will enter their employee ID on the application screen, then time spent on tasks by each employee in the warehouses and total man-hours will be recorded, collected, and stored into a data cloud [5]. The combination of data from TTS and the existing warehouse management system (WMS) enables the company to gauge the productivity of each employee and each operational process in their warehouse. The effort has resulted in data delivery that has enabled the managers to plan the resources allocation and predict truck departure times more accurately.
Digital transformation technology adoption failure
Boston Consulting Group conducted a study in 2020 and found that 70% of digital transformation projects struggled to meet their goals [6]. In another report by IDC, it was mentioned that one of the factors that hold back digital transformation effort is digital innovation in APEJ (Asia Pacific except for Japan) is not coordinated across the organization and is treated as a special project and siloed initiatives. Departments in the organization also operate as siloed entities and do not have processes visibility which hinders dynamic collaboration between multiple teams and stakeholders, hence preventing innovations. Digitization efforts made by the City of Ghent in Belgium is a good example to demonstrate that a silo mentality in the organization would lead to early digital investments that do not yield results [7]. In 2014, the City of Ghent decided to integrate BPM lifecycle into the digitization effort of their service processes (i.e., taxes, environment, and citizen’s affairs) after facing customer complaints due to complex digital services where each department provided their own web services requiring customers to deal with multiple IDs and passwords.
Moreover, lack of process visibility also leads to poor decision-making due to inability to derive opportunity when organization operation process flowcharts are absent. The risk without effective process management, the technology adoption may not be able to deliver maximum value to the business and is likely to fail after two or three years. This is due to the obscurity in assessing the risks and setting and managing relevant KPIs to digital transformation efforts, which is elementary in the agile transformation method.
Can BPM guarantee technology adoption success?
When we cook, we certainly need the main ingredients to make the dish happen, but we also need to have a “secret” sauce or seasoning for a better taste. Cooking burgers, for instance, patty and bread are the main ingredients but the sauce spread on the patty would differ the taste. When a company decides to embark on a digital transformation agenda, it needs to map the journey with a clear goal and BPM is a method to map the digital transformation journey. Therefore, BPM is one of the main components or ingredients to ensure technology adoption success. Meanwhile, talents and personalized data-driven culture unique to the business sector are the “secret” sauces that play a critical role to better performing in this digital age.
Coming back to the City of Ghent digitization example, in brief, the City of Ghent successfully escaped from the silo where BPMN diagrams were designed to begin while implementing BPM lifecycle throughout their digital innovation in the organization. After having comprehensive business processes, existing processes were improvised and based on digitization principles which they called “building blocks” approach. All services translated into their custom pilot digital chains project (taxes, environment, and civic affairs). Digitization projects were run collaboratively by a business and an IT project manager. In 2016, preliminary results indicated a surge in the number of digital transactions at the City of Ghent compared to prior integration of BPM. The percentage of digital tax submissions increased from 5.5% (2014) to 28.9% (2016).
Another case study is Sparda-Bank Hamburg [8], which adopted BPM as a method to achieve process transparency and provide centralized access to each department. By doing so they were able to identify weak points in their processes where different offices were handling the same processes differently. They utilized the iGrafx BPMN tool which helped them increase visibility, allowing new technology adoption linked to the processes and the successful digitization of subprocesses.
Takeaway points
In a nutshell, processes are an elementary part of digitization, digitalization, and digital transformation effort in businesses and organizations. Ambidextrous BPM is a recommended method to harness digital technologies to pursue innovation and to establish sustainable digital transformation initiatives. Likewise, BPM enables organizations to decipher end-to-end processes and provide insight and accurate data to identify potential processes that eventually support strategic alignment, allowing businesses and organizations to better respond to disruptive technologies in this digital age.
References
[1]https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/strategy-and-corporate-finance/our-insights/how-covid-19-has-pushed-companies-over-the-technology-tipping-point-and-transformed-business-forever
[2] https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prUS46967420
[3] https://hbr.org/2021/11/the-essential-components-of-digital-transformation
[4] Business process management. In: Wiley encyclopedia of management, vol 7. Management information systems. doi:10.1002/9781118785317.weom070213
[5] https://online.logi-biz.com/49224/ (JP)
[6] https://www.bcg.com/publications/2020/increasing-odds-of-success-in-digital-transformation
[7] https://www.researchgate.net/publication/319067082_Kiss_the_Documents_How_the_City_of_Ghent_Digitizes_Its_Service_Processes
[8] https://www.igrafx.com/casestudies/sparda-bank-hamburg/
